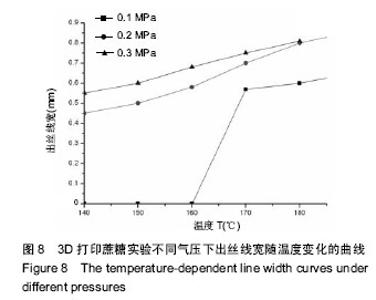
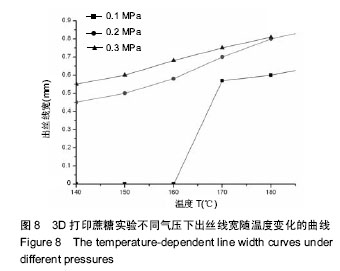
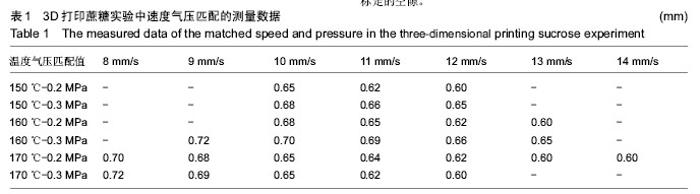
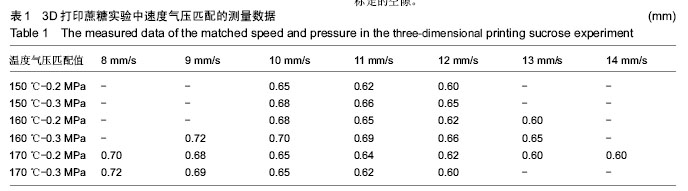
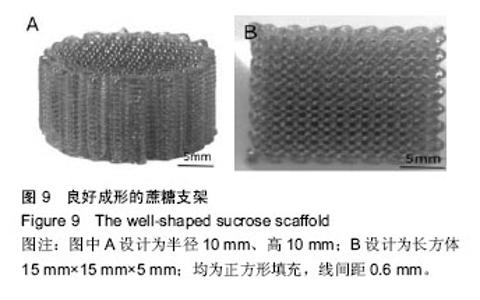
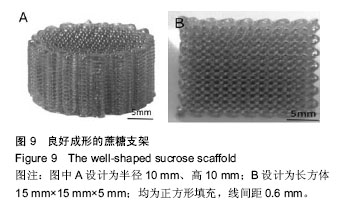
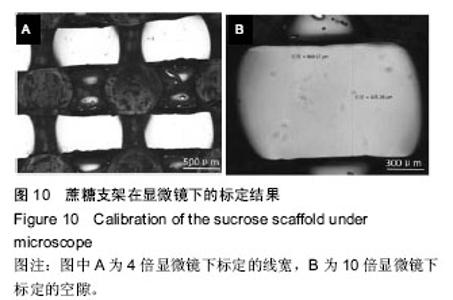
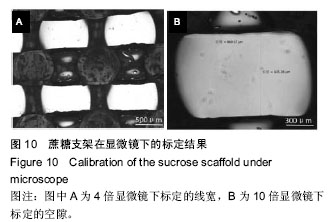
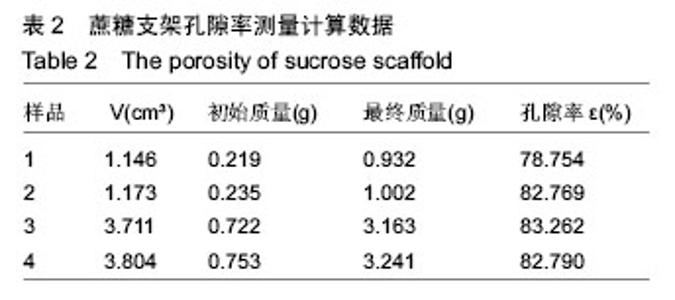
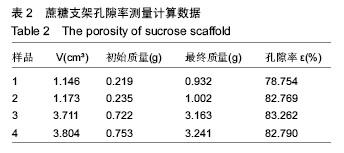
| [1] 宋晓美.快速成形技术的特性分析及应用研究[J].机电工程技术,2015,44(9):58-60.[2] 刘晓辉.快速成型技术发展综述[J].农业装备与车辆工程, 2008,46(2):10-13.[3] 李秋爽.快速成型技术在医学领域的应用研究[D].山东大学,2008.[4] 连芩,李涤尘,陈成,等.面向组织工程化软组织的制造技术及增材制造[J].中国组织工程研究, 2014,18(8):1263-1269.[5] 黄霞,陈家昌,申长雨,等.骨组织工程支架材料研究进展[J].化工新型材料,2010,38(9):65-68.[6] 郑欣,陈一心,邱旭升,等.快速成型技术在骨组织工程中的应用进展[J].中国矫形外科杂志, 2014,22(24):2244-2247.[7] 杨久林,谢红国,于炜婷,等.组织工程用壳聚糖研究进展[J].功能材料,2013,44(11):1521-1525.[8] 胡涛,徐铭恩,严明,等.不同比例聚乳酸羟基乙酸复合骨支架的低温沉积制造及性能[J].中国组织工程研究, 2015, 19(12):1805-1811.[9] 索海瑞,岳秀艳,史廷春,等.高分子生物材料快速成形构建组织工程支架的研究[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复, 2008,12(6):1101-1106.[10] Billiet T,Gevaert E,De Schryver T,et al. The 3D pringting of gelatin methacrylamide cell- laden tissue-engineered constructs with high cell vialility. Biomaterials.2014;(35):49-62.[11] 覃泽林,孔令孜,李小红,等.广西蔗糖产业发展竞争力分析[J].南方农业学报,2015,46(4):722-728.[12] 王立升,郭鑫,刘力恒,等.医药级蔗糖制备工艺研究[J].食品科技,2008,33(7):148-150.[13] 吴其晔,巫静安.高分子材料流变学[M].北京:高等教育出版社,2002.[14] 郭健.浅析差示扫描量热法测定材料的比热容[J].太原科技,2007,165(10):19-20.[15] 尹应梅.基于DMA法的沥青混合料动态粘弹特性及剪切模量预估方法研究[D].华南理工大学,2011.[16] 黄友如,华欲飞,裘爱泳.差示扫描量热技术及其在大豆蛋白分析中的应用[J].粮食加工,2004,29(2):58-61.[17] 许鑫,马永强,姚姗姗,等.SEM DSC和RVA在豆类淀粉研究中应用[J].农产品加工•学刊, 2010,9(9):44-47.[18] 卓蓉晖,胡言,陈文怡.用不同方法测定材料的玻璃化转变温度[J].现代仪器,2004, 10(4):25-26.[19] 陈中中,早热木,李涤尘,等.利用快速成型技术制造人工生物活性骨[J].西安交通大学学报,2003,37(3):273-276.[20] DongNN.Study of carbohydrate compounds at different temperatures by pyrolysis-gas chrometography-mass spectrometry.J Chin Mass Spec Soc. 2004;25(1):24-28.[21] Xiong Z,Yan Y,Wang S,et al.Fabricationofporous scaffolds for bone tissue engineering via low temperature deposition.Scripta Materialia. 2002;46(11): 771-776.[22] 索海瑞,岳秀艳,史廷春,等.组织工程支架的低温沉积制造工艺参数研究[J].机电工程,2009,26(3):57-60.[23] 屈晨光,张师军,高达利,等.环境温度对3D打印成型精度的影响[J].塑料工业,2015, 43(8):53-55.[24] 梁宪涛.3D打印喷头的温度分析及控制策略研究[J].黑龙江科技信息,2015,17(32):195.[25] 罗楠,王泉,刘红霞.一种快速3D打印分层方向确定算法[J].西安交通大学学报,2015, 49(5):140-146.[26] 赵辰.3D打印机分层软件的设计与实现[D].东南大学, 2009. |